5 Botox Danger Zones to Avoid
David Fuller
Last Updated On: October 16, 2024
Botox is one of the most sought-after rejuvenation procedures. It is the first thing that comes to mind when people think about smoothing out wrinkles.
There is a lot of talk about fillers, both in a positive and negative context. There are fantastic results of rejuvenation with fillers, and there are cases where the consequences are horrendous, such as vision deterioration. Why does this happen?
The doctor who performs plastic surgery and injection procedures must intricately know the human anatomy, particularly the face, as they must know the many dangerous Botox areas.
If patients have Botox injections into these hazardous areas, the consequences of the injections can be irreversible. So today, we will discuss how to avoid Botox injection danger zones.
What is Botox?
Botox is a highly purified botulinum toxin formulation derived from Clostridium botulinum. Although botulinum toxin is a potent neurotoxin, health professionals can safely administer it in low doses to treat various medical and cosmetic conditions, such as wrinkles, through its ability to block nerve signals in the injected muscle, leading to temporary paralysis.
Botox has been approved for several medical and cosmetic indications, including:
- Cosmetic use: Botox is commonly used to treat dynamic wrinkles (wrinkles caused by repetitive muscle movement) in the face, such as frown lines, crow’s feet, and forehead lines.
- Neurological disorders: Botox is also used to treat muscle spasticity in conditions such as cerebral palsy, stroke, or multiple sclerosis. It can help reduce muscle stiffness, pain, and involuntary movements.
- Eye disorders: Botox can treat strabismus (crossed eyes) or blepharospasm (involuntary eyelid twitching). By relaxing the affected muscles, Botox can improve eye alignment and reduce spasms.
- Headaches: Botox reduces the frequency and severity of chronic migraines or tension headaches. It works by blocking the release of pain neurotransmitters in the brain.
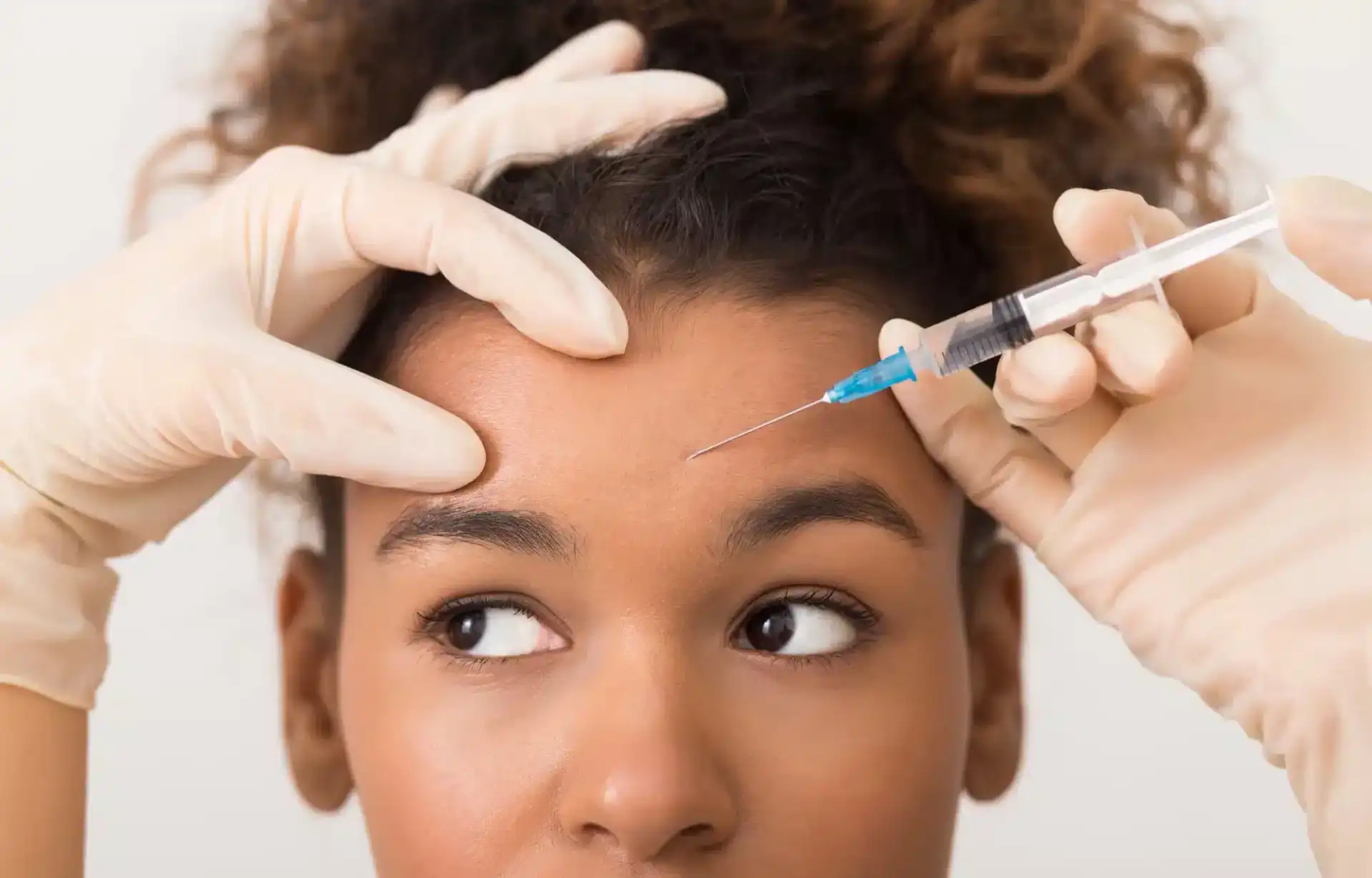
Danger Zones of Botox Injections
When performing Botox injections, healthcare providers must know safe injection zones to minimize the risk of complications. The upper third of the face, including the forehead, glabella, and crow’s feet, is generally considered a safe zone for Botox injections.
To avoid potential complications, healthcare providers should avoid injecting Botox in these high-risk or danger zones:
- Eye area (orbicularis oculi muscle and the corrugator supercilii muscle): The eye area is one of the face’s most sensitive and delicate areas. Injecting Botox too close to the eye can cause drooping of the eyelid (ptosis) and affect the eye’s ability to close properly, which can cause dryness, eye irritation, and, in severe cases, even vision impairment.
- Forehead (The frontalis muscle): Injecting Botox too low on the forehead can cause drooping of the eyebrows, which can create an unappealing, tired, or sad appearance. Injecting Botox too high on the forehead can lead to a “Spock-like” look with raised brows.
- Nasolabial folds and lips: Injecting Botox in the nasolabial folds (lines that extend from the nose to the corners of the mouth) and lips can leave the patient with difficulty speaking and smiling, as well as an unnatural appearance.
- Neck and chin: Injecting Botox in the neck and chin can cause muscle weakness and difficulty swallowing. In severe cases, it can lead to aspiration pneumonia.
- Temples: Injecting Botox in the temples can lead to temporary or permanent changes in vision, such as blurred or double vision.
A doctor must be appropriately trained and have an excellent knowledge of anatomy to inject Botox safely. Botox is a potent neurotoxin that can have severe consequences if injected incorrectly.
A properly trained and licensed healthcare professional, such as a dermatologist or plastic surgeon, will have received specialized training in administering Botox injections.
They will be familiar with the anatomy of the face, including the location and function of the facial muscles, and will identify dangerous Botox zones to avoid.
Any trained healthcare professional will know precisely the proper technique to use when injecting Botox, including the dosage and injection site best suited to the patient and results required. They will also be able to provide advice to patients on the care process for before and after the injection, to minimize the risk of complications.
Six Popular Dermal Filler Trends in 2023 – read more.
How to Avoid Botox Complications
Here are some critical steps that healthcare professionals should take to avoid complications when administering Botox injections:
- Properly assess the patient. Before administering Botox injections, healthcare professionals should thoroughly evaluate their medical history and any medications they are taking. They should also examine the patient’s facial anatomy to identify danger zones and determine the best injection sites.
- Use sterile equipment. All equipment used during the Botox injection procedure should be sterile and single-use, including needles, syringes, and vials.
- Properly prepare the injection site. Healthcare professionals should properly clean and disinfect the injection site before injecting Botox. It minimizes the risk of infection.
- Use the correct dosage. Healthcare professionals should use the correct dosage of Botox for the specific treatment area. It can help to avoid over-injection and potential complications.
- Properly inject Botox. Healthcare professionals should use proper injection techniques, such as the correct depth and angle for the injection site. The professional will adequately distribute the Botox, avoiding the risk of complications.
- Provide post-injection care instructions. Healthcare professionals should provide patients with post-injection care instructions, including avoiding certain activities and medications, and any potential side effects they may experience.
- Follow up with patients. Healthcare professionals should follow up with patients after the procedure to ensure they are not experiencing any complications and that Botox works effectively.
A good doctor requires more than just knowing the dangerous areas to understand how to inject the medication correctly to minimize the likelihood of complications.
Here are some tips for proper Botox injection technique and minimizing risks:
- Identify the injection site. Before injecting Botox, healthcare professionals should identify the correct site based on the patient’s anatomy and treatment goals. The professional should then appropriately mark the injection site to ensure accuracy.
- Use proper needle size. The needle size used for Botox injections should be appropriate for the injection site and depth. The healthcare professional typically uses a smaller needle size for superficial injections; and a larger one for deeper injections.
- Use proper injection technique. The healthcare professional should inject the needle at a 90-degree angle to the skin and inject the Botox slowly while withdrawing the needle; they should then gently massage the injection site after the injection to distribute the Botox and minimize the risk of bleeding.
- Avoid over-injection. Over-injection can lead to a frozen or unnatural appearance. Healthcare professionals should use the correct dosage of Botox for the specific treatment area and avoid injecting too much Botox into one spot.
- Monitor the patient for adverse effects. After the injection, patients should be monitored for adverse effects, such as excessive swelling or bruising, infection, or allergic reactions. Patients should also avoid certain activities, such as strenuous exercise, for several hours after the injection.
- Use sterile equipment. All equipment used during the injection procedure should be sterile and single-use, including needles, syringes, and vials. Sterility minimizes the risk of infection.
- Educate the patient.The healthcare professional should educate the patients about the potential dangers and benefits of Botox injections and proper aftercare instructions, advising them to report any unusual symptoms or side effects immediately.
Proper patient selection and informed consent are essential for safe and effective Botox treatment. Healthcare professionals should carefully consider each patient’s needs and ensure they understand the procedure before proceeding.
Please note: Botulinum toxins are muscle relaxants intended to be injected directly into the muscle to achieve the desired effect. Botox injected too superficially is ineffective, as there will be no noticeable effect.
Conclusion
For medical professionals, it is crucial to provide safe and effective treatments to patients. The best way is to stay updated on the latest developments and follow best practices for safe injection techniques. By being informed, a doctor can offer the most advanced and effective treatments while minimizing the risk of complications.
References
- Brennan C. (2014). Avoiding the “danger zones” when injecting neurotoxins. Plastic surgical nursing: official journal of the American Society of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgical Nurses, 34(4), 173–178. https://doi.org/10.1097/PSN.0000000000000064
- Benedetto, A. (Ed.). (2011). Botulinum Toxins in Clinical Aesthetic Practice (2nd ed.). CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.3109/9781841847559
- Seckel BR. Facial Danger Zones: Avoiding Nerve Injury in Facial Plastic Surgery. Canadian Journal of Plastic Surgery. 1994;2(2):59-66. https://doi.org/10.1177/229255039400200207
- Shah, R. (2017, April 12). 10 botox mistakes you should avoid when injecting Botulinum toxin. HSI. https://www.theharleystreet.com/journal/10-botox-mistakes-you-should-avoid/
FAQ
Where should you not get Botox?
Danger zones to avoid when injecting Botox: the Frontalis muscle, Eye area, Nasolabial folds and lips, Chin muscles, and Temples (superficial temporal artery).
Where not to inject Botox in the forehead?
When having a Botox injection into the forehead, the healthcare professional should avoid the orbicularis oculi muscle, corrugator supercilii muscle, and frontalis muscle.
How common are complications from Botox?
According to ASPS (American Society of Plastic Surgeons), the overall complication rate from Botox injections is less than 1%.
Products
Cart
Log In
Newsletter
Subscribe for exclusive offers and updates on new arrivals
Share feedback at:
Working Hours
MON - SUN 9AM to 6PM EST
The Most Popular Brands
Med Supply Solutions
Support
Secure checkout is guaranteed with full adherence to PCI DSS payment standards.
Products listed here are guaranteed authentic and manufacturer-sourced.
Pay easily with trusted providers


Copyright 2025. Med Supply Solutions